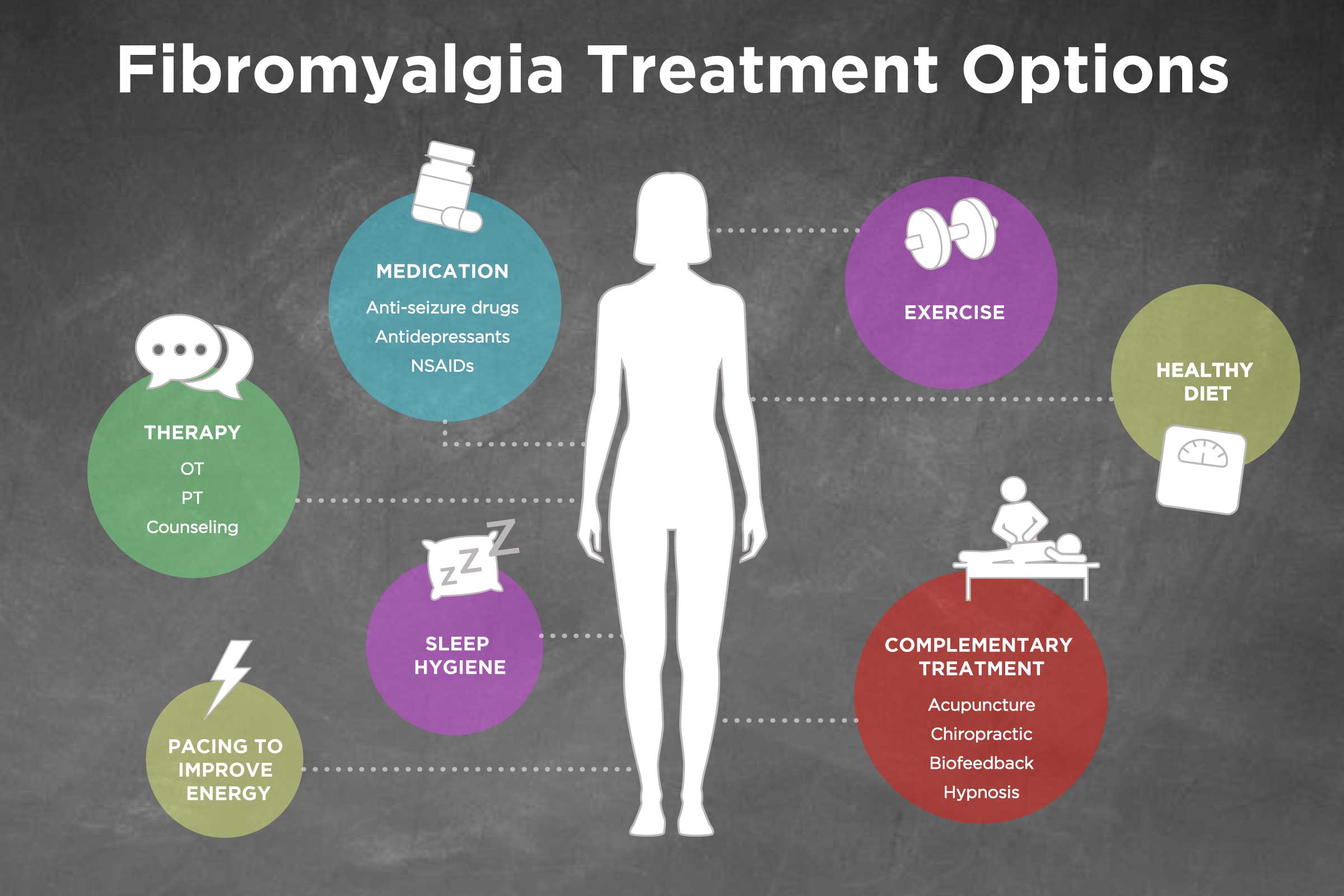
Neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia are terrible illnesses that impact millions of individuals worldwide. They drastically reduce quality of life, frequently resulting in chronic pain, sleep difficulties, and mental suffering. Managing these problems can be difficult, necessitating a complex strategy that may involve medication, lifestyle changes, and psychological therapies. Pregabalin, a medicine often used to treat neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia, has emerged as an important aid in managing both illnesses. In this detailed guide, we will look at the function of pregabalin solution in treating neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia, including its mechanism of action, dose, efficacy, safety concerns, and practical advice for patients and healthcare professionals.
Understanding Pregabalin’s Mechanism of Action
Pregabalin, often known as Lyrica, is a gabapentinoid medicine. It was first design as an antiepileptic medication but has now been license to treat neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and other diseases. Pregabalin works largely by binding to the α2δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system. This binding inhibits the release of various neurotransmitters, including glutamate, norepinephrine, and substance P, which are important in pain signaling and neuronal excitability.
Pregabalin modulates neurotransmitter release, reducing central nervous system neuron hyperexcitability, pain signal transmission, and neuropathy and fibromyalgia symptoms. Additionally, it enhances the mood and sleep of individuals with these disorders, thereby contributing to its therapeutic properties.
Pregabalin: Dosage and Administration.
Lyrica (Pregabalin) is available in a variety of forms, including capsules, pills, and oral solutions. Patients who have difficulties swallowing capsules or pills may choose pregabalin solution since it allows for more flexible dosage. The suggested dose of pregabalin solution for the treatment of neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia is 75 mg given orally twice day. However, dose may differ depending on specific patient characteristics, such as the severity of symptoms and responsiveness to treatment.
Healthcare providers should start pregabalin therapy with a low dose and progressively increase it based on efficacy and tolerability. The highest daily dose of pregabalin for neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia is usually 300 mg, split into two or three doses. Patients with renal impairment may need to alter their dose because pregabalin is predominantly absorb through the kidneys.
Pregabalin solution should be taken with meals to increase absorption and reduce gastrointestinal adverse effects. Patients should adhere to their healthcare provider’s dose and administration guidelines and avoid suddenly terminating pregabalin medication, as this may raise the risk of withdrawal symptoms.
Pregabalin’s efficacy in fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain
Pregabalin has been shown in clinical research to effectively reduce neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia symptoms. In randomized controlled trials, pregabalin relieved pain better than placebo in those with diabetic neuropathy, post herpetic neuralgia, and fibromyalgia.
For example, Research published in the journal Pain Medicine looked at the efficacy of pregabalin in fibromyalgia patients and discovered that pregabalin-treated patients had much lower pain levels than placebo patients. Studies show that pregabalin can lower pain intensity, enhance sleep, and improve functioning in neuropathic pain syndrome patients.
Pregabalin’s effectiveness in neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia is hypothesize to arise from its capacity to control neurotransmitter release and diminish neuronal hyperexcitability in the central nervous system. Pregabalin treats these diseases by addressing numerous pain processing systems.
Safety Concerns and Side Effects
Pregabalin is typically well accepted, however it can have negative effects in certain people. Pregabalin’s most common adverse effects are dizziness, somnolence, dry mouth, weight gain, and peripheral edema. These adverse effects are often mild to moderate in severity and improve with time as the body responds to the medicine.
Patients should be encourage to report any troublesome or persistent side effects to their doctor. In addition to its possible negative effects, pregabalin is prone to dependency and misuse, especially in people with a history of drug abuse or addiction. Healthcare professionals should constantly monitor patients for symptoms of abuse or dependency, and prescribe pregabalin with caution in these groups.
Pregabalin may potentially interact with other drugs, such as opioids, benzodiazepines, and alcohol, which depress the central nervous system. Pregabalin combined with these drugs can raise the risk of respiratory depression and central nervous system depression. Healthcare professionals should carefully weigh the risks and advantages of administering pregabalin in combination with other drugs, and patients should be continuously monitor for evidence of drug interactions.
Practical Tips for Patients
Patients receiving pregabalin solution for neuropathic pain or fibromyalgia can take numerous actions to improve treatment success and reduce adverse effects.
Dosage Instructions: Take the pregabalin solution as directed by your healthcare practitioner. Do not exceed the suggested dosage or suddenly quit therapy without seeing your doctor.
Take pregabalin solution with meals to increase absorption and reduce gastrointestinal adverse effects.
Monitor for adverse Effects: Keep track of any adverse effects you may have while taking pregabalin solution and report them to your doctor.
Avoid Alcohol and CNS Depressants: While using pregabalin solution, do not consume alcohol or take any other drugs that depress the central nervous system, since this might raise the risk of unpleasant effects.
Communicate with your healthcare provider. Keep your healthcare provider updated on your symptoms, treatment progress, and any changes in your health condition.
Conclusion
Pregabalin 150 solution is an effective drug for managing neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. Pregabalin alleviates symptoms in these situations by regulating neurotransmitter release and lowering neuronal hyperexcitability in the central nervous system. Healthcare providers should weigh the risks and benefits of pregabalin and closely monitor patients to ensure safe and effective therapy. Pregabalin solution patients should follow their doctor’s dose and administration instructions and report any concerns or side effects immediately.. Pregabalin solution, when used properly, can assist people with neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia enhance their quality of life.



I am always looking online for articles that can assist me. Thank you!